 Software
Software
BPM Cyber Platform
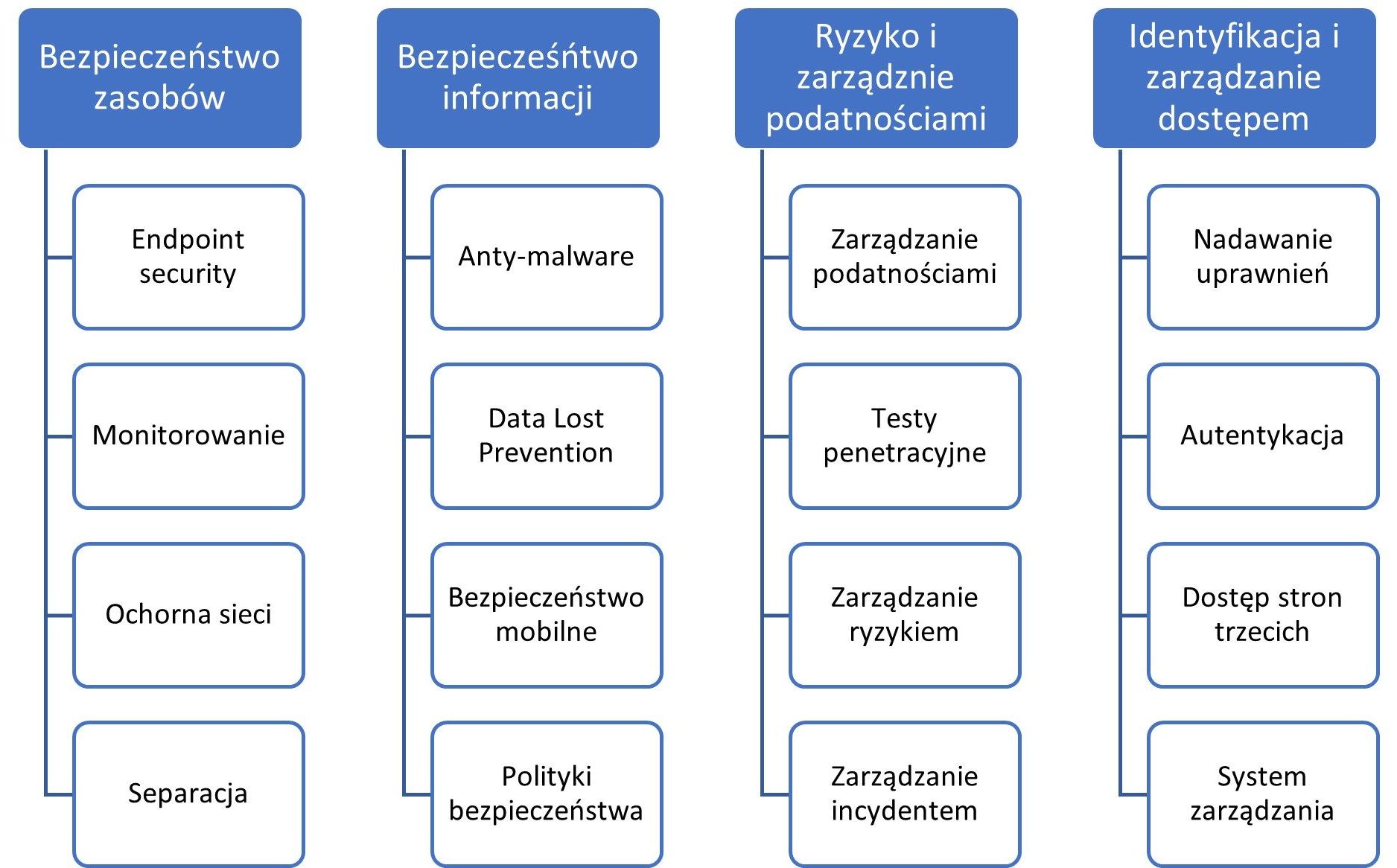
Our complete cybersecurity ecosystem provides:
- Inventory of assets and identification of connections,
- Defining roles and responsibilities, ensuring awareness
- Assessment of the materiality of assets thanks to,
- Security assessment through,
- Automated risk analysis thanks to implemented algorithms,
- Planning of improvement activities
- Monitoring and evaluation of the effectiveness of activities:
- Management of the problem, incident, non-conformities, emergency situation,
- Cybersecurity status monitoring and reporting
Do you want to enter a higher level of cybersecurity?
BPM Cyber Platform provides answers to the following questions:
- What to protect?
- How to protect?
- Is the security effective?
- What to do in the event of an incident and failure?
- What is the level of user awareness?
- What is the security level of the organization?
We will integrate security and ensure the integrity of operations, without the need to replace your current systems and security.

Want to take your cybersecurity to the next level?
BPM Cyber Platform provides answers to the following questions:
- What to protect?
- How to protect?
- Is the security effective?
- What to do in case of incident and failure?
- What is the user awareness level?
- What is the security level of the organization?
We will integrate security and ensure the integrity of operations, without the need to replace your current systems and security.
There are many reasons why an audit should be considered. Usually, it is carried out when important technology decisions or business requirements are made. Here are some potential reasons why you should consider conducting a network audit.
1) Outdated and incomplete inventories
When was the last time an audit was carried out? A lot can change over time – organizational changes, new and existing web application requirements, budget and capital expenditure forecasting, and rotation in the IT department, especially in the network infrastructure.
2) Updates and Refresh
Network administrators tend to fall into an operational state where their day-to-day operations are their top priority. However, networks need to be updated and refreshed from time to time. This is especially true for the modernization of network technology. This includes performing an audit to identify hardware and software that need to be replaced or upgraded.
3) Troubleshooting and troubleshooting
Probably the last thing IT professionals or network administrators would like to hear is that we have a major network failure, cannot connect to the Internet, or latency issues are affecting applications, customers, users and partners. In this scenario, it is needed in an emergency as a way to fix network problems.
4) Regulatory and Compliance Standards
For many industries, including financial and healthcare, regulatory and compliance standards are an important reason to start a network audit. This includes adhering to HIPAA, SOC1, SOC2, FedRAMP, PCI, FISMA, NIST and other critical compliance standards. It can be used by internal or external auditors to assess the compliance of the organization as a whole.
- Definition of roles
- Assessment of the materiality of assets thanks to:
- Information classification
- Business Impact Analysis
- Assign a goal
Vulnerability Management aims to find the weaknesses of an organization or an ICT system. This vulnerability could be exploited by an attacker. The vulnerability management process is based on systematic verification of the security of organizations and systems. We evaluate the detected gap and decide on appropriate action measures. A vulnerability is a security gap or a misconfiguration of the ICT system that allows for an effective attack. Consequently, it leads to the loss of confidentiality, integrity and availability of information. The aim is to monitor the infrastructure and provide comprehensive support from the moment of vulnerability identification to the moment of protecting the environment.
Providing comprehensive support from the moment of vulnerability identification to the moment of protecting the environment. Vulnerability management is a service of identification, verification and support in the implementation of appropriate action in the event of a security vulnerability. The service is provided based on passive and active vulnerability scanning in defined time periods.
The service includes:
- passive identification of known vulnerabilities,
- active identification of vulnerabilities in specific, cyclical time windows,
- analysis of identified vulnerabilities (confirmation of existence,
- use risk estimation),
- communication with IT services about the risk related to the identified vulnerability,
- development of recommendations,
- implementation of recommendations and verification after patching the gap
Built-in algorithms calculate the risk based on:
- identified assets and relationships
- validity of processed data and supported processes
- vulnerability analysis
- incident and event history
- tests performed
The system supports making decisions related to risk.
The system supports the planning of activities related to:
-
- vulnerabilities
- risk
- inconsistencies
- incidents
- improvement actions
- SOC / NOC recommendations
It provides action scenarios, playbooks, and automates execution.
The system enables the connection of external sources: SOC, DLP, console, in order to monitor events and unify management. Allows:
- Monitor indicators
- Plan and implement audits
- Plan and implement continuity tests
- Perform pentests
Penetration tests are aimed at finding gaps in the IT systems and IT network of an organization, which may or may not be used consciously or not to cause loss of ICT security parameters. These are periodic tests in the context of data confidentiality, integrity, availability and authenticity. As in the Vulnerability Management service, they detect a vulnerability, but focus on actively exploiting it to threaten the organization.
The system periodically tests the infrastructure and provides comprehensive support from the moment the problem is identified until the environment is secured.
Automatic pentests – these are application and system tests performed automatically, without the participation of experts and consultants. After logging in to the testing system, the customer has the option to pre-configure the test, using a simple survey, to indicate the test subject, and the system will perform it automatically, generating a test report with preliminary recommendations.






